An AI knowledge graph connects your brand’s entities, facts and relationships into a structured semantic network that AI systems trust and reuse. This guide explains how AI builds graph connections, which brand nodes matter most, and how to design, map and audit your own graph for stronger visibility across Google and LLM-powered search.
Building an AI Knowledge Graph
Search is no longer about pages alone. Modern AI systems build meaning by connecting entitiesm people, brands, products, and topics into networks they can reason over. If your brand is not clearly connected inside these networks, AI struggles to understand who you are, what you do and why you matter.
That’s where an AI knowledge graph becomes essential. It acts as the backbone of semantic trust, aligning your brand across websites, platforms and data sources so AI can confidently reference and recommend you.
What is an AI knowledge graph?
An AI knowledge graph is a structured representation of entities and the relationships between them. Instead of treating content as isolated text, AI systems map facts into nodes (entities) and edges (relationships).
For example:
- A brand node connects to services, founders, locations, reviews and expertise areas.
- A service node connects to use cases, industries and supporting content.
- A person node connects to credentials, publications and affiliations.
In practice, this means AI can answer questions not by ranking URLs, but by traversing a semantic network that feels consistent and trustworthy. The concept builds on ideas formalized in Google Knowledge Graph Papers, where entities and relationships replace keyword-only relevance.
How AI builds graph connections
AI does not manually “crawl” a graph you submit. It infers graph structure from repeated, consistent signals across the web.
Key mechanisms AI uses
- Entity recognition: Identifying names, brands, people, products and concepts in text.
- Relationship inference: Detecting patterns like “Company X provides Service Y” or “Person A founded Brand B.”
- Cross-source validation: Confirming that the same facts appear on multiple trusted sources.
- Contextual reinforcement: Strengthening edges when entities appear together consistently in meaningful contexts.
If your brand description, services, or leadership differ across platforms, AI creates weak or conflicting edges. Over time, this reduces trust and reuse.
Key nodes your brand must control
Every entity graph SEO effort starts with controlling the most important nodes in your brand’s semantic network.
Core brand nodes
- Brand entity: Official name, description, category and positioning.
- People entities: Founders, leadership, authors, subject-matter experts.
- Service or product entities: Clearly defined offerings with consistent naming.
- Location entities: Cities, regions and service areas tied to your brand.
- Topical authority entities: Core subjects your brand is known for.
These nodes should remain stable across:
- Your website
- Author bios
- Social profiles
- Business listings
- High-quality third-party mentions
Consistency here allows AI to build dense, confident graph connections rather than fragmented ones.
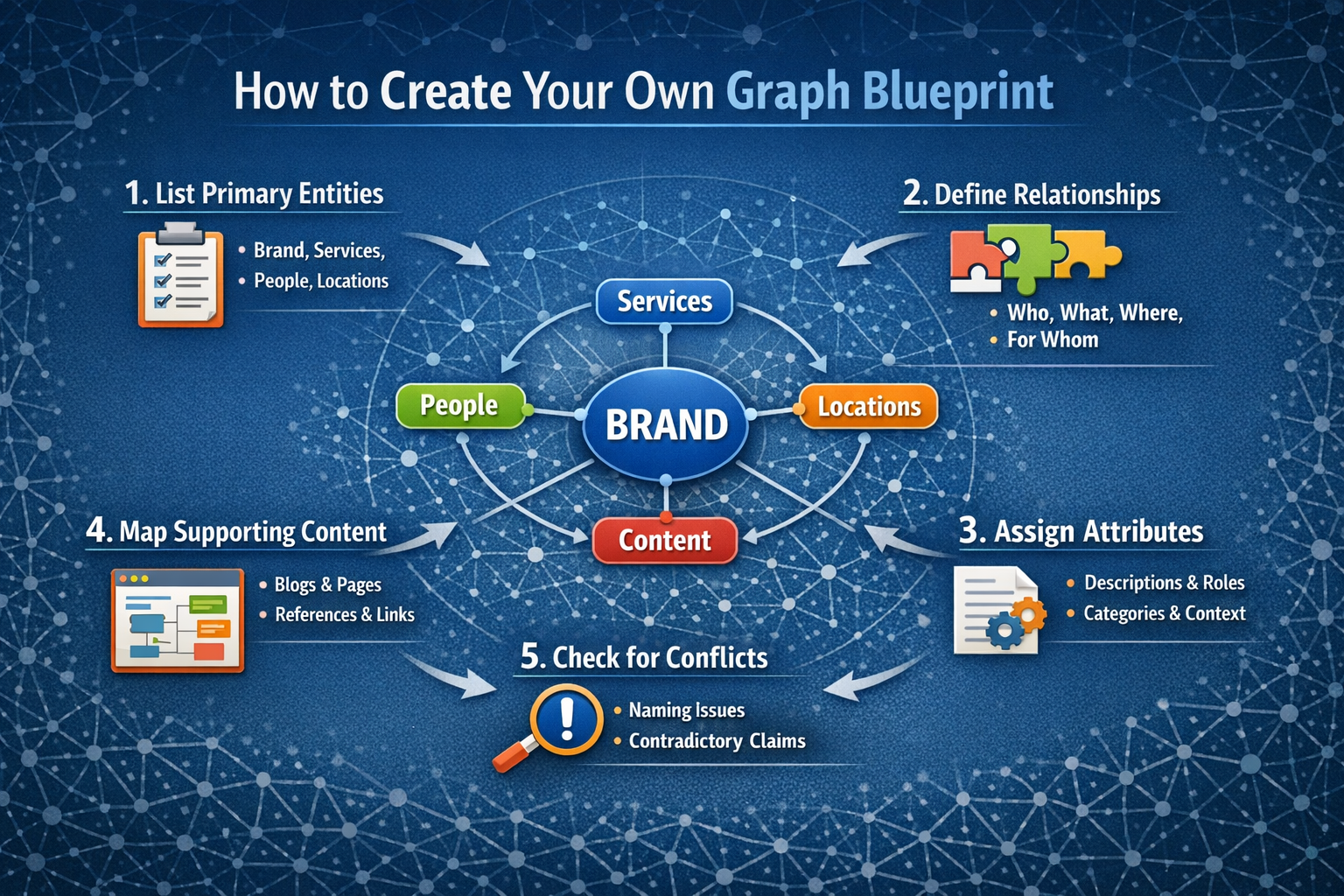
How to create your own graph blueprint
Before optimizing content or schema, you need a blueprint a visual and logical plan for how your brand graph engineering should look.
Step-by-step blueprint process
- List primary entities: Brand, services, people, locations.
- Define relationships: Who provides what, where and for whom.
- Assign attributes: Descriptions, credentials, categories and context.
- Map supporting content: Blogs, pages and references that reinforce each node.
- Check for conflicts: Remove naming variations and contradictory claims.
This blueprint becomes your reference point for content creation, internal linking, schema markup and off-site optimization.
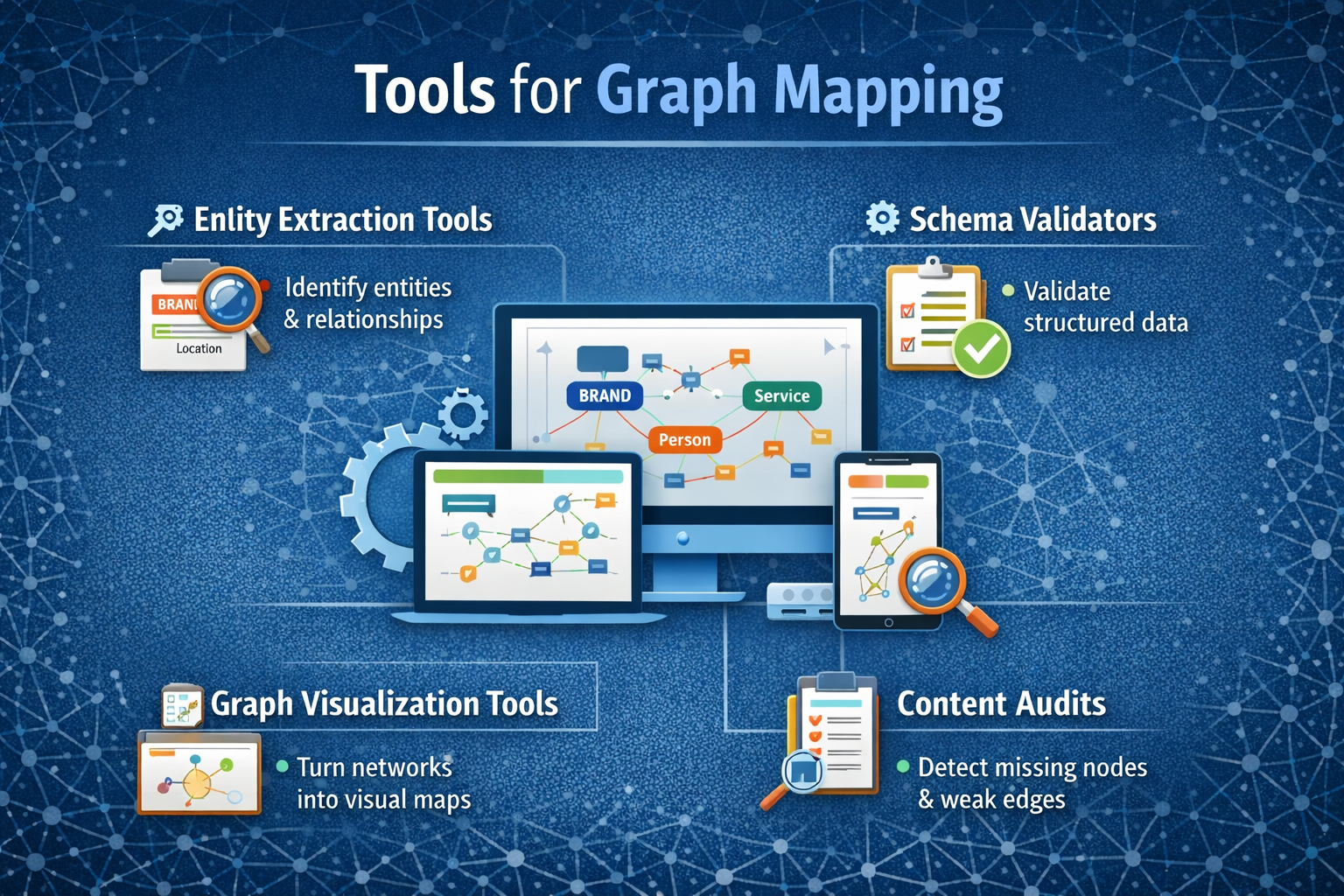
Tools for graph mapping
You don’t need enterprise-level infrastructure to start mapping a semantic network AIO. Several tools help visualize and validate entity relationships.
Practical tool categories
- Entity extraction tools: Identify entities and relationships within your content.
- Schema validators: Ensure structured data aligns with your graph blueprint.
- Graph visualization tools: Turn entities and relationships into visual maps.
- Content audits: Detect inconsistent naming, missing nodes, or weak edges.
When used together, these tools reveal where AI may struggle to connect your brand meaningfully.
Checklist
Use this checklist to assess whether your AI knowledge graph is strong enough for modern AI-driven search:
- Brand name and description are consistent everywhere
- Services and offerings are clearly defined as entities
- People and authors are connected to expertise and content
- Internal links reinforce entity relationships
- Structured data matches on-page claims
- External mentions support the same facts
- No conflicting brand or service terminology
- The graph blueprint is documented and updated
If multiple boxes remain unchecked, AI likely sees your brand as fragmented.
FAQs
How do I build a knowledge graph?
Start by identifying your core brand, people, services and location entities. Define how they relate, then ensure those relationships are consistently reflected across your website, structured data and external mentions.
Why does an AI knowledge graph matter for SEO?
AI-driven search relies on entity relationships rather than keywords alone. A strong knowledge graph helps AI trust your brand, reuse your information and surface you more often in answers.
What is the difference between entity SEO and traditional SEO?
Traditional SEO focuses on pages and keywords, while entity SEO focuses on meaning and relationships. Entity-based optimization aligns better with how modern AI systems understand content.
Do I need a schema to build a knowledge graph?
Schema is not mandatory, but it significantly improves clarity. Structured data makes your entities and relationships explicit, reducing ambiguity for AI systems.

